Accurate Vector Mixer Measurements with a Vector Network Analyzer
November 13, 2024
1 Introduction
Frequency-translating devices such as mixers and converters are fundamental building blocks of most RF and microwave communication systems. Accurately characterizing the performance of these devices is a critical factor in the design process. The frequency offset function provided by Siglent SNA series allows the source to work at the mixer’s input frequency while the receiver alternates operation between the mixer’s input and output frequencies. Since phase comparison of different frequencies is meaningless, the phase characteristics of frequency conversion device cannot be obtained. This technique is called scalar mixer measurement. To obtain the phase characteristics of a mixer, we need to use vector mixer measurement techniques.
2 Small Signal Model of Mixers
Since phase is a relative value, its measurement requires a reference baseline. Co-frequency devices can be directly characterized by the phase difference between the input and output signals to insert the phase shift. While mixers have different input and output frequencies, they cannot be directly compared in phase, and its phase characteristics are very much related to the operating mode, so a clear definition of the phase characteristic model of a mixer is needed before exploring its test method.
The output signal of a mixer contains multiple spectrum components. Take fundamental frequency mixing as an example, the input signal of mixer be denoted as IN and the local oscillator as LO. The mathematical expression for multiplying the two signals can be described as follows:
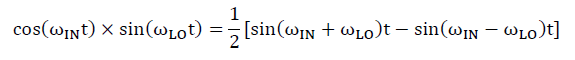
Thus the output will have frequency elements at the sum and difference of the two input signals. LO signal has many harmonics (all odd if it is symmetrical signal) and so there will also be outputs at the sum and difference of each of the harmonics of the signals with the input signal as well, sometimes referred to as intermodulation spurs, or higher-order products. Designers extracts the required frequency components at the output through filtering according to actual needs. To simplify the analysis, the mixers mentioned below are all in fundamental mixing mode. If the frequency of the filtered output signal is higher than that of the input signal, it is defined as an upconverter, and if the frequency of the output signal is lower than that of the input signal, it is a downconverter.
Click to download the article.
