Gain Compression Measurements with the SNA Network Analyzer
November 13, 2024
1 Introduction
As the core components of a system, amplifiers are widely used in various RF and microwave systems. Amplifiers have a linear gain region where the input power and output power are linearly related. The gain in this region is referred to as linear gain (also known as small-signal gain). As the input power is increased to a level that causes amplifier to approach saturation, the gain will decrease. The 1 dB gain compression is defined as the input power level that causes amplifier gain to drop 1 dB relative to the linear gain. The gain compression function is to determine the compression power of amplifier at various frequency points within a specified frequency range and to measure the parameters at that point.
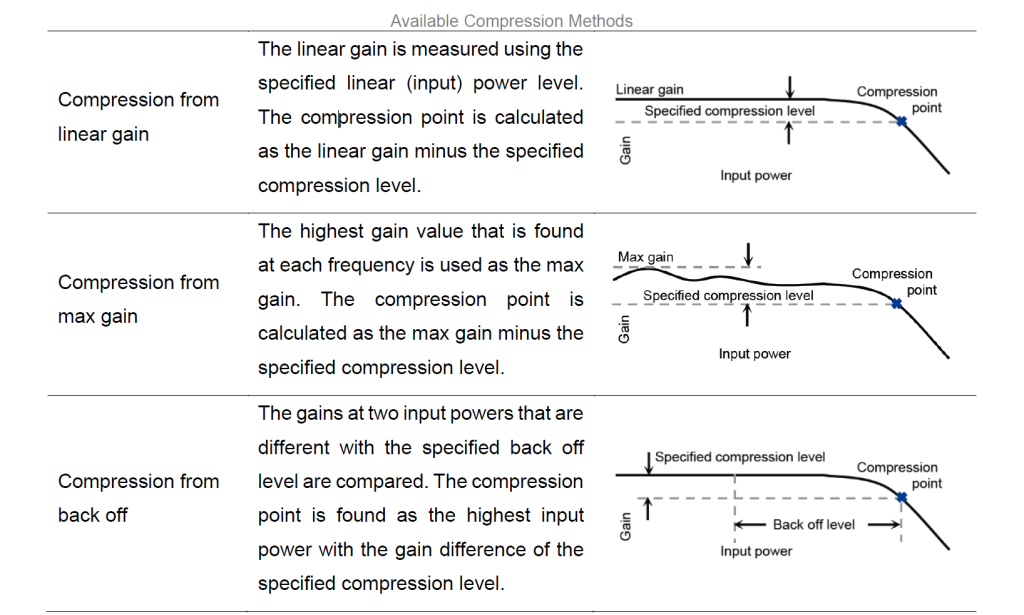
2 Compression Definitions
When introducing the compression point in the previous section, it was mentioned that the point where the gain decreases by 1 dB relative to the reference gain is identified as the compression point. The reference gain here refers to the linear gain. However, the selection of the reference gain can vary in different situations. Based on the selection of the reference point, compression can be classified as Compression from Linear Gain, Compression from Max Gain, Compression from Back Off, X/Y Compression, and Compression from Saturation.